STEAM LOCOMOTIVES
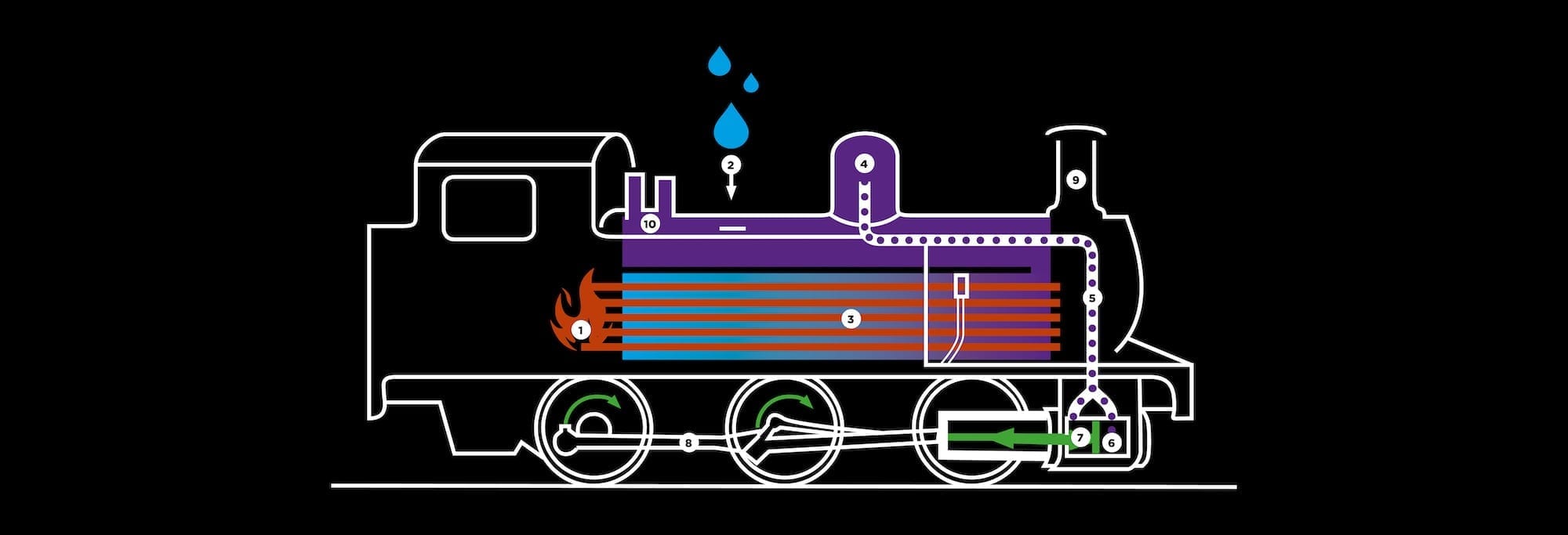
THE OPERATION OF A STEAM LOCOMOTIVE
The firebox (1) contains the fire, which is essential to the operation of the locomotive. Cold water (2) is heated by the tubes (3) and turns into steam. It becomes light and accumulates in the dome (4) from where it is routed (5) in more or less quantity in the cylinders (6). The steam pushes the pistons (7) in one direction and then in the other. The latter carries with it the embalming (8) and the wheels of the machine. The chimney (9) expels exhausts composed of steam and smoke by sizing the fire. Safety valves (10) allow the rapid expulsion of excess steam if too much pressure builds up in the boiler.
SANDY
Type 131
Commissioning: 1984
MECKLENBURG
Type 040
Commissioning: 1991
HARZ
Type 131
Commissioning: 2007
MÖLM
Type 030
Commissioning: 1984
STUART
Type 030
Commissioning: 1990
FO 1
Type HG 3/4
Commissioning: 2010
CALIFORNIA
Type Mallet
Commissioning:1993
SPREEWALD I
Type 130
Commissioning: 2006
SPREEWALD II
Type 130
Commissioning:2006
WALDENBURG
Type G 3/3
Commissioning: 1992
Type of locomotive
ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVES
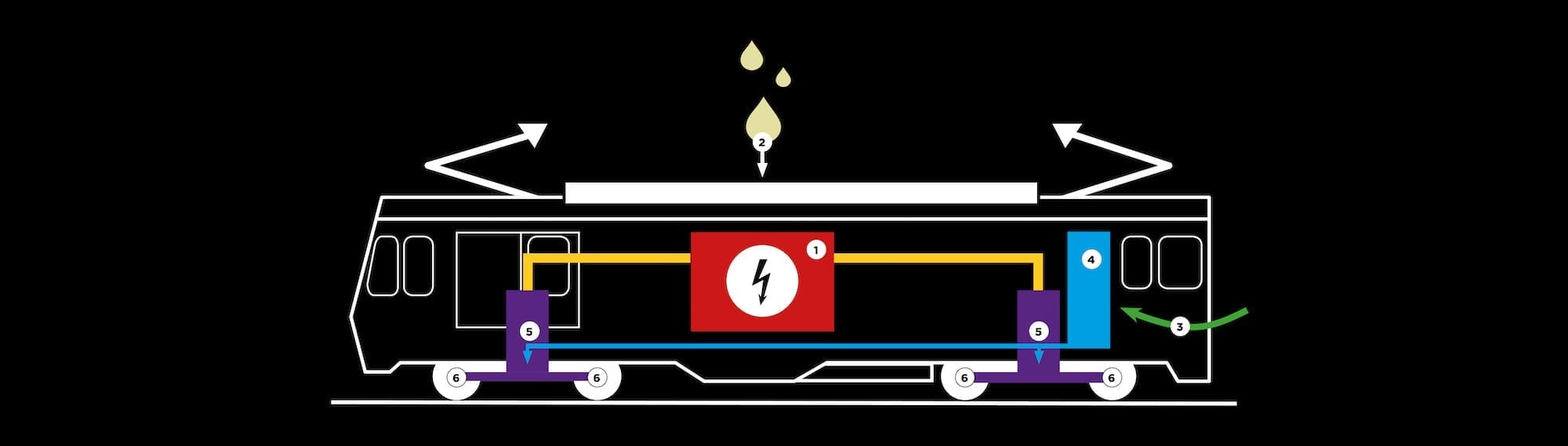
THE OPERATION OF AN ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVE
The so-called “electric” locomotives operate thanks to a generator (1) petrol (2). Informations from the driver’s cab are (3) processed by an automaton (4) that intern regulates the two electric motors (5) placed above the two bogies. The engines drive the axles (6) using a chain.
MGN
Type HGe 2/2
Commissioning:
2003
MOB
Type Ge 4/4 II
Commissioning:
1993
MGB
Type Ge 4/4 III
Commissioning:
1990
AL
Type BDeh 4/4
Commissioning:
1992
FO 32
Type HGe 4/4
Commissioning: 2013
RhB
Type Ge 6/6 I
Commissioning: 2008
WB
Type He 2/2
Commissioning: 2005
AMTRAK
Type 2x P42
Commissioning: 2001
TPC
BDeh 4/4
Commissioning: 1991
